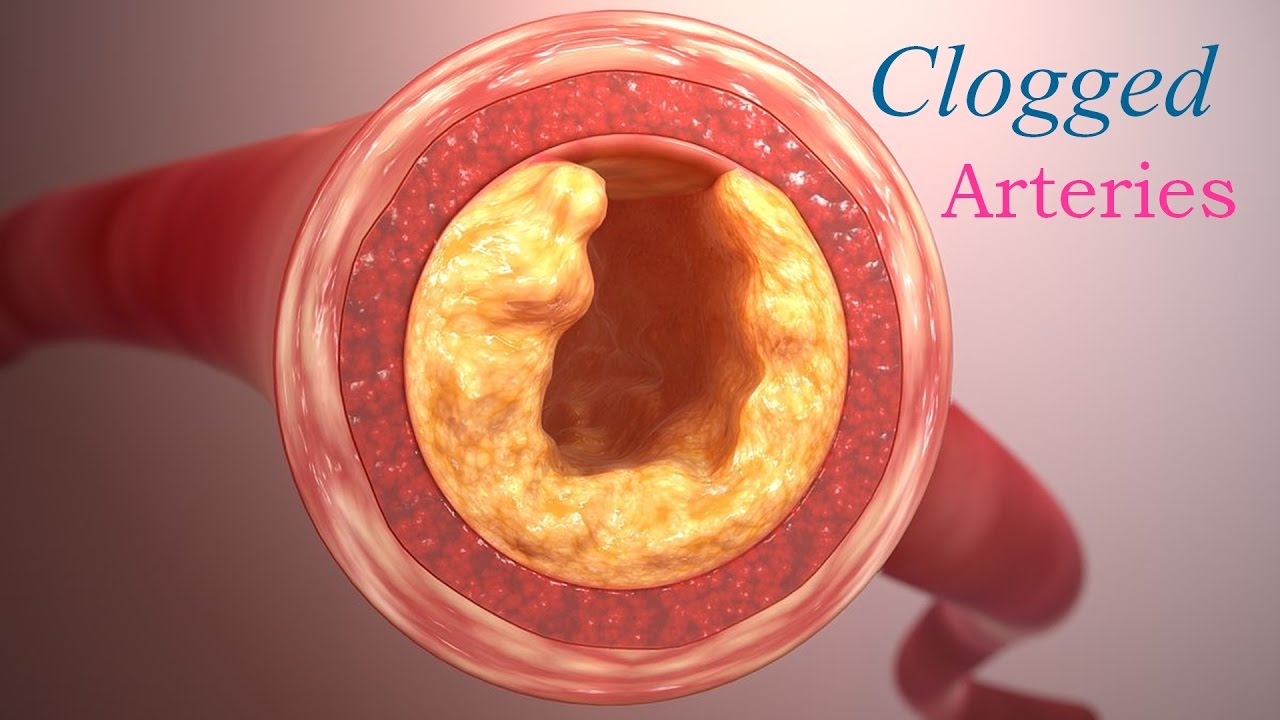
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood throughout the body. This blood is rich in oxygen, and it is transported from the heart to every part of the body, including the brain and the toe. Healthy arteries have smoother inner walls for blood to flow easily through them, but sometimes, due to bad diet and other lifestyle factors, there can be accumulations of plaque in these vessels. It gets accumulated on the walls of these vessels and results in an impaired flow of blood. Arterial plaque, in some cases, can even block the arteries completely. These clogged or blocked arteries increase the likelihood of heart-related issues, such as heart attack, stroke, and even death.
What are the symptoms of clogged arteries?
In many cases, the clogged arteries do not cause any symptoms until a big event such as heart attack or stroke occurs, but warning signs can help prevent it.
At other times, when the artery is blocked by 70%, the build-up of the plaque may give the following –
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Weakness or dizziness
- Nausea
- Sweating
The first symptom is most commonly chest pain, is also called angina. It results from reduced blood flow to the heart. This is because of the arteries that lead to the heart being clogged. This results in transient ischemic attacks or TIAs. The following symptoms might be there –
- The sensation of weakness/numbness on either side of the body
- Inability to move an arm or a leg
- Loss of vision on either side
- Slurring of words
What causes arterial plaque?
Plaque accumulates on the inner walls of the arteries is made of various particles that circulate with the blood. These can be fats, calcium, cholesterol, cellular waste, and fibrin. To cure this arterial clogging, the walls also release different substances, that worsen the situation eventually. This condition is called atherosclerosis, and it results in more and more narrowing of the vessels, along with them becoming hard.
Although there are a lot of reasons behind this build-up, a few can be –
- High ”bad” cholesterol and low ”good” cholesterol. High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) are among the major contributors to arterial plaque formation. People with low ”good” cholesterol, or high-density lipoprotein (HDL) circulating in the blood, are also at a higher risk.
- High blood pressure – Having a constantly high blood pressure increases the chances of arterial plaque build-up. This increased pressure also allows for more hardening of the clogged vessels resulting in a worsened condition.
- Cigarette smoke – Cigarette smoke is directly proportional to the increase in atherosclerosis in the arteries of the heart, legs, and the aorta.
- Diabetes – having an elevated level of circulating blood sugar in the body is a significant culprit. It results in more increased problems, such as metabolic syndrome and organ insufficiencies. Increased levels of blood sugar also result in an increased risk for atherosclerosis.
- Other risks include family history, stress, a sedentary lifestyle, and being overweight.
- Knowing about family history is also critical.
What are the complications that can arise because of clogged arteries?
The level of complications depends on the depth of arterial plaque accumulation. Clogged arteries in different parts of the body lead to different medical conditions, including:
- Coronary artery disease. When plaque accumulates in the arteries that carry blood to the heart, it increases the chances of a heart attack. This is one of the leading causes of death in the United States.
- Carotid artery disease. The carotid arteries run on either side of the neck. Their task is to supply oxygen to the brain. Plaque in these arteries can lead to stroke.
- Peripheral artery disease. If plaque is present in the peripheral arteries, it leads to gangrene of the feet.
Clogged arteries if found in the peripheral artery can result in causing –
- Leg pain
- Delayed healing of leg injuries
- Cold feet
- Gangrene
Are there tests to diagnose clogged arteries?
There are a number of tests for clogged arteries. The doctor determines which test has to prescribed based on the symptoms and medical history. They include:
- Cholesterol screening
- Chest X-ray
- CT scan
- Ultrasound
- Echocardiogram or stress test
- Electrocardiogram
- MRI or PET scanning
- Angiogram
How are clogged arteries or arterial plaque treated?
The best cardiac hospitals in India advise for the following modifications and treatments for arterial plaque –
1. Lifestyle modification –
- Eating a diet that is low in saturated fats and cholesterol, having fewer sugars and simple carbohydrates. Diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Not smoking
- Exercising regularly
- Managing stress levels
- Keeping blood pressure under control
- Maintaining low blood sugars
-
2. Interventional procedures –
- Stent surgery
- Bypass surgery
- Balloon angioplasty
3. Medications –
Medications that help in reducing the accumulation of arterial plaque can be –
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs
- Blood pressure-lowering drugs
- Aspirin and other blood-thinning drugs, to reduce the possibility of clot formation